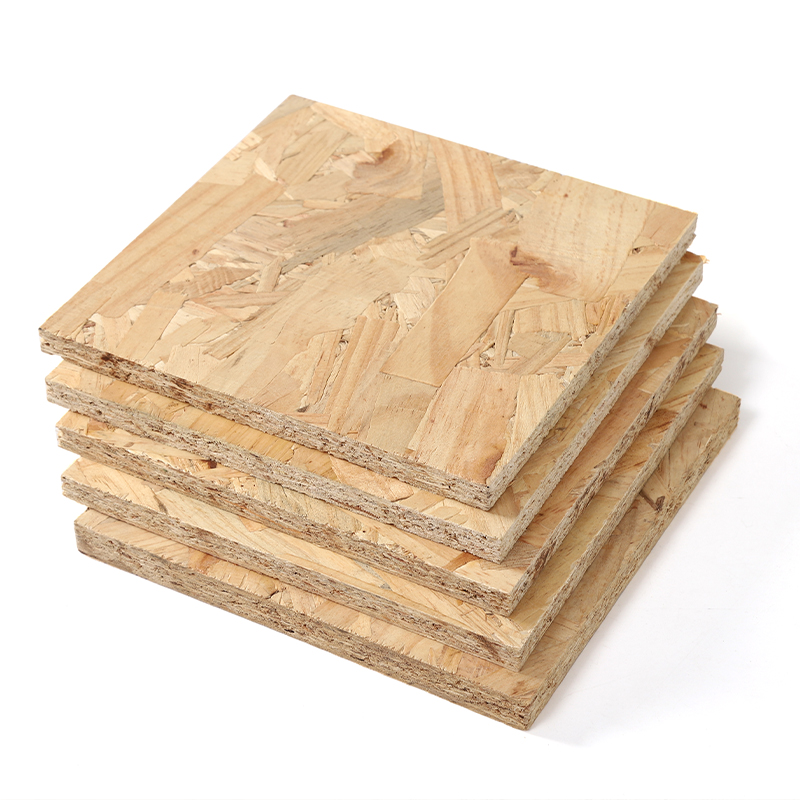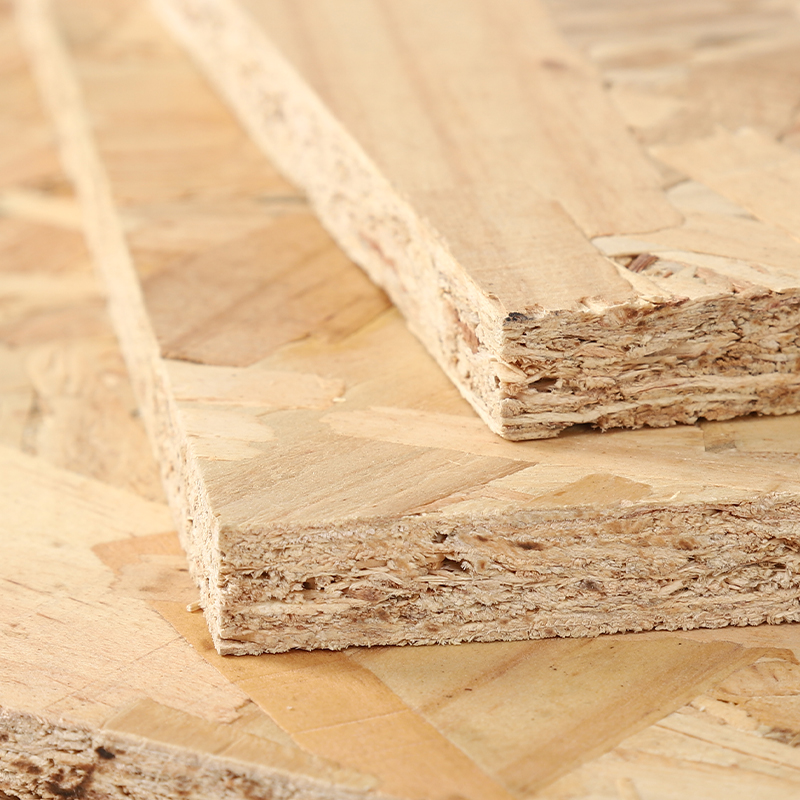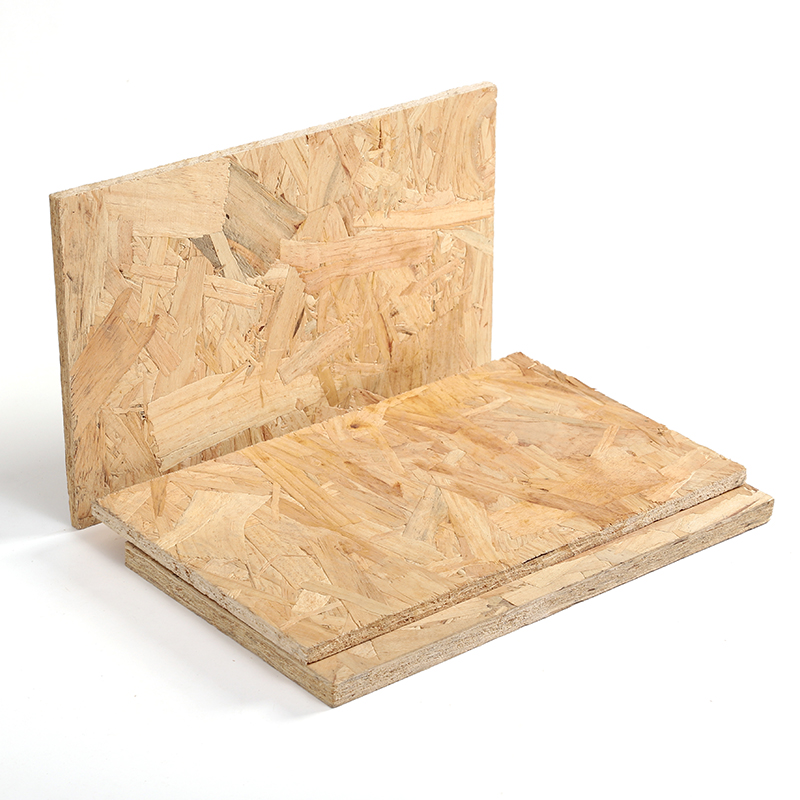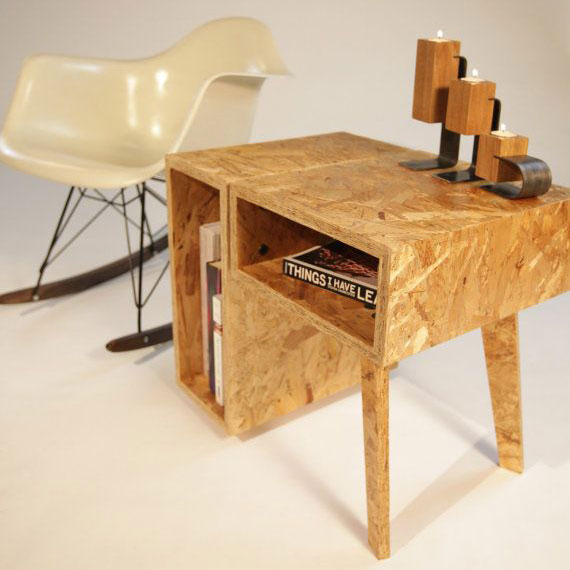
17MM MDI OSB Outdoor Decoration
Brand YZY
Product origin Linyi
Delivery time 14 Days
Supply capacity 10Containers/14 days
osb 3 boards
Oriented strand board (OSB) Oriented strand board is a type of engineered wood similar to particle board, formed by adding adhesives and then compressing layers of wood strands (flakes) in specific orientations.
What is OSB2, OSB3 and OSB4?
OSB2: MR glue, it can be used in dry environment and with weight capacity, such as packing and construction.
OSB3: Melamine glue, it can be used in moisture environment and with weight capacity, such as outdoor and indoor construction.
OSB4: WBP glue, it can be used in external wall coverage, roof coverage, flooring base, ceiling construction insulation.
OSB is a material with favorable mechanical properties that make it particularly suitable for load-bearing applications in construction. It is now more popular than plywood, commanding 66% of the structural panel market. The most common uses are as sheathing in walls, flooring, and roof decking. For exterior wall applications, panels are available with a radiant-barrier layer laminated to one side; this eases installation and increases energy performance of the building envelope. OSB is also used in furniture production.
Product Name | OSB,Oriented Stranded Board |
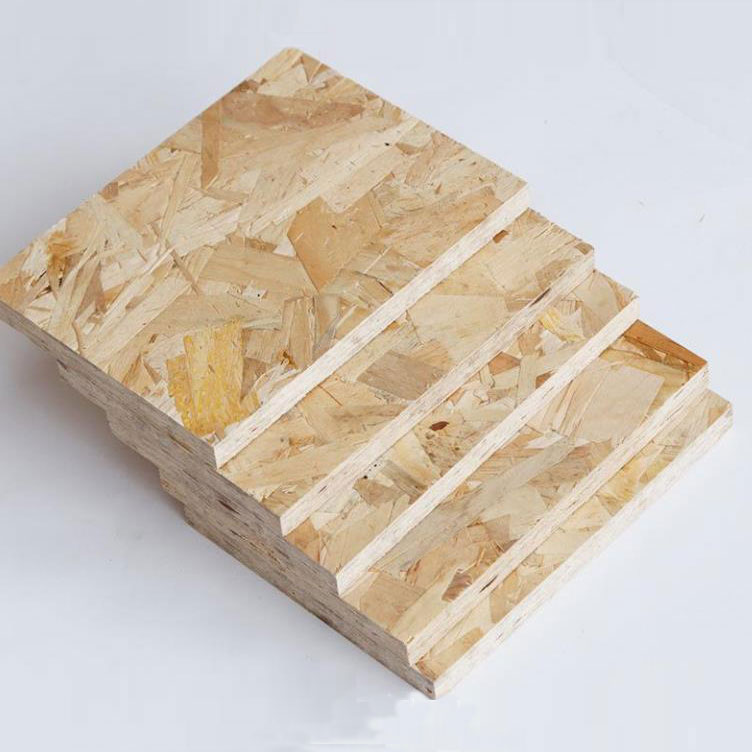
Size | 1220*2440mm or other size as per customer's request |
Thickness | 6-25mm |
Core | Poplar,Combi.,Pine,Hardwood |
Glue Type | E0,E1,E2,Melamine and WBP |
Application | Construction,Packaging,Furniture and Decoration |
MOQ | 1*20ft Container |
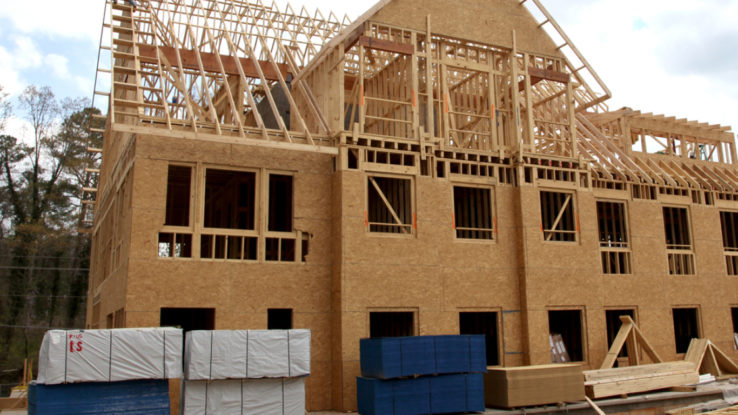

· OSB/2 – Load-bearing boards for use in dry conditions
· OSB/3 – Load-bearing boards for use in humid conditions
· OSB/4 – Heavy-duty load-bearing boards for use in humid conditions
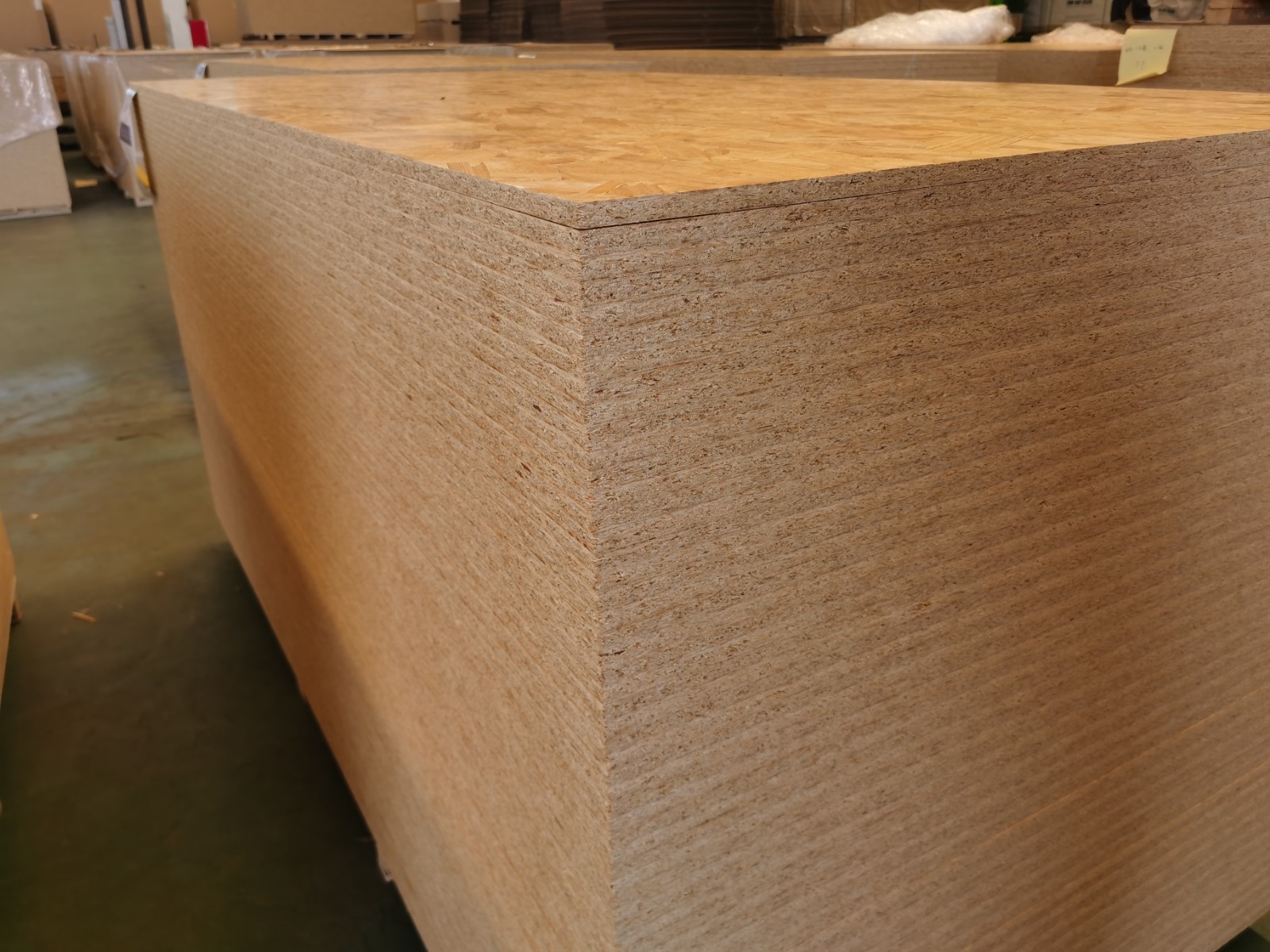

OSB Waterproofing vs. Water Resistance
In construction, understanding the difference between waterproofing and water resistance is essential, especially when working with wood-based materials like Oriented Strand Board (OSB). These terms are often used to describe how well a material can handle exposure to moisture and prevent damage. While some materials are designed to be fully waterproof, OSB is neither waterproof nor inherently water resistant without additional treatments. This makes proper understanding and protection vital when using OSB in environments where moisture is a concern.
Water Interaction with OSB
Like most wood-based products, OSB is susceptible to moisture absorption, leading to expansion and contraction as the wood fibers interact with water and humidity. When moisture infiltrates the wood strands that make up OSB, it can cause the material to swell. Over time, if OSB is exposed to consistent moisture without adequate protection, the process of delamination can occur.
Delamination refers to the breakdown of the bonds between the wood strands, weakening the structure of the board. This occurs as water interferes with the adhesive used to bind the strands together, causing it to lose its grip. As a result, the OSB loses both its structural integrity and load-bearing capacity, leading to potential failure in its intended application.
The Role of Waxes and Additives
To improve OSB's ability to resist moisture, manufacturers often add waxes or other moisture-resistant additives during the production process. These substances create a thin protective barrier on the surface of the OSB, helping to repel water and reduce moisture absorption. Waxes, in particular, coat the board’s surface and strands, helping to prevent moisture from penetrating deep into the wood fibers.
However, it is important to note that while these treatments can enhance the water resistance of OSB, they do not make it fully waterproof. Over time, if OSB is exposed to significant or prolonged moisture, even with a wax coating, the material may still experience damage or swelling. The waxes help extend the board's lifespan in humid or damp conditions, but they cannot prevent water damage entirely.
Practical Applications and Considerations
When using OSB in construction projects, especially those where the material may be exposed to moisture—such as roofing, wall sheathing, or subflooring—builders should take precautions to protect the OSB. Although waxes and additives provide some water resistance, it's crucial to add additional waterproofing layers if the material will be exposed to the elements for long periods.
This could involve:
Waterproof coatings or sealing agents applied post-installation to create a stronger moisture barrier.
Membranes or waterproof sheathing wraps to protect the OSB in exterior applications.
Regular maintenance and inspections to ensure the protective layers remain intact and effective over time.
Conclusion
Understanding the limitations of OSB in terms of waterproofing and water resistance is key to ensuring the longevity of your construction projects. While OSB can be treated with waxes and additives to enhance its moisture resistance, it is not inherently waterproof. For applications where OSB will be exposed to moisture or humidity, it’s important to take extra steps, such as adding waterproof coatings, to protect the material from water damage. Proper treatment and ongoing maintenance can help mitigate the risks associated with moisture exposure, preserving the structural integrity of the OSB and extending its useful life.
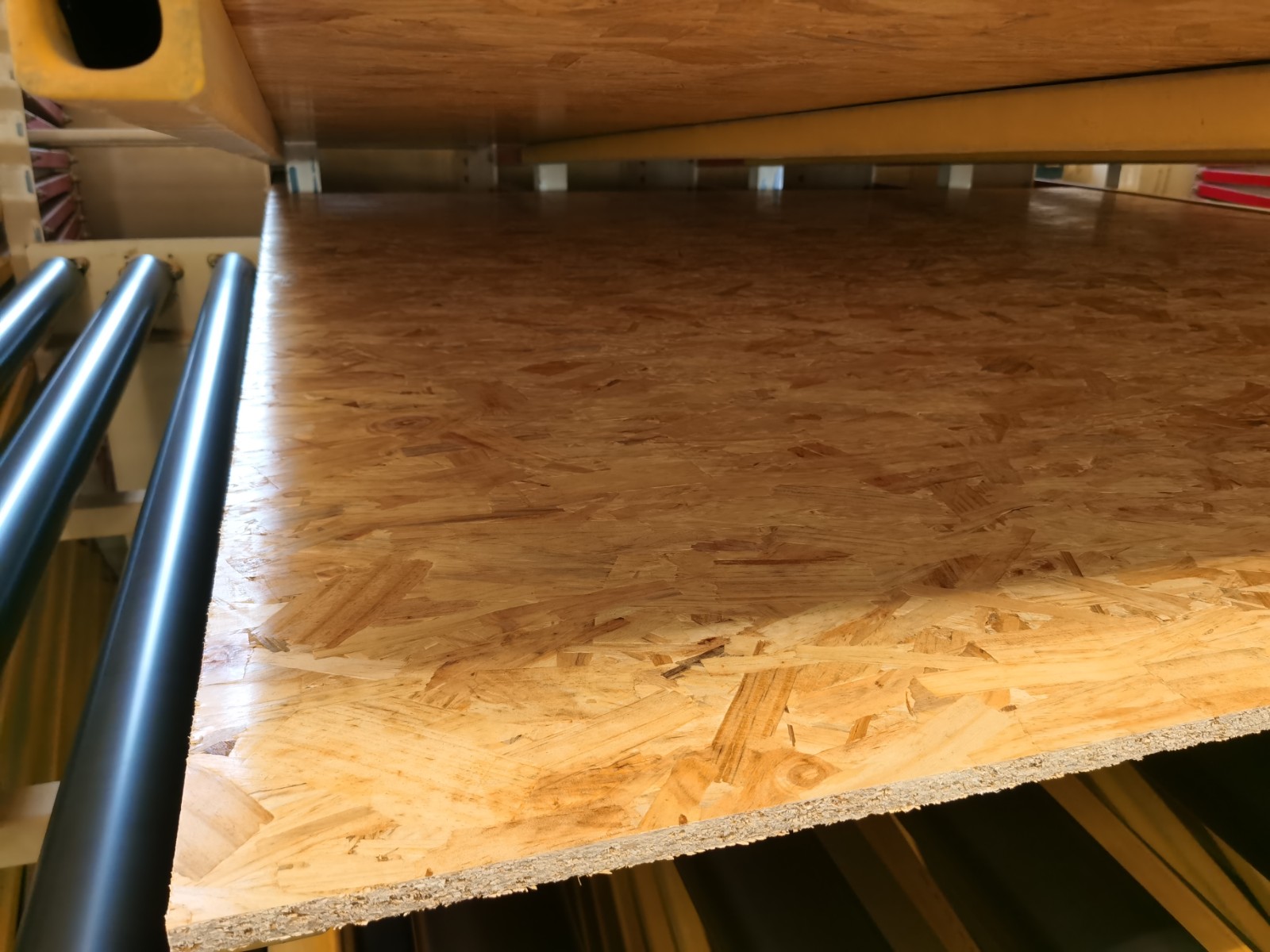
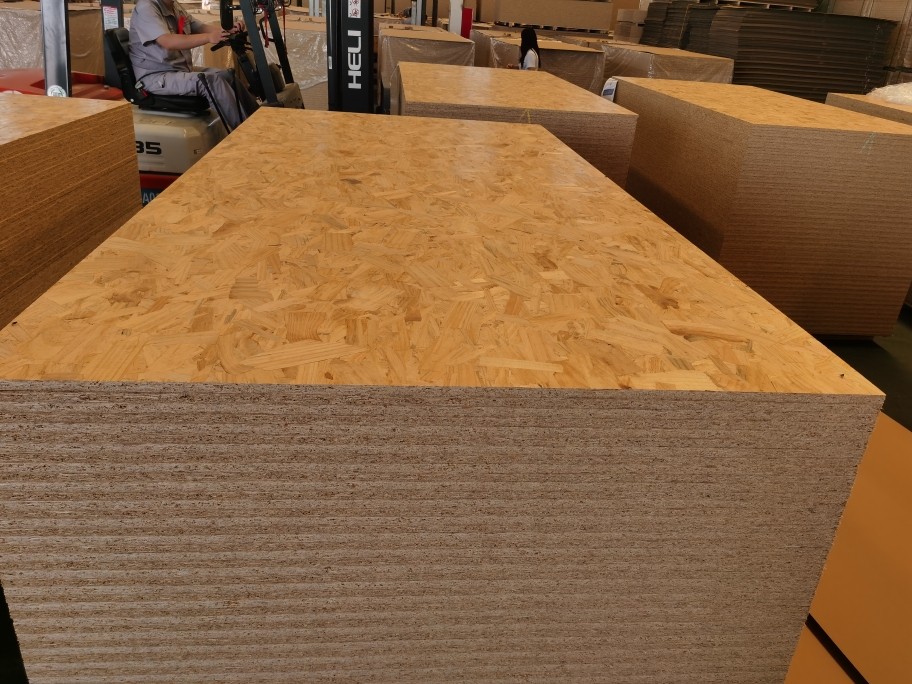
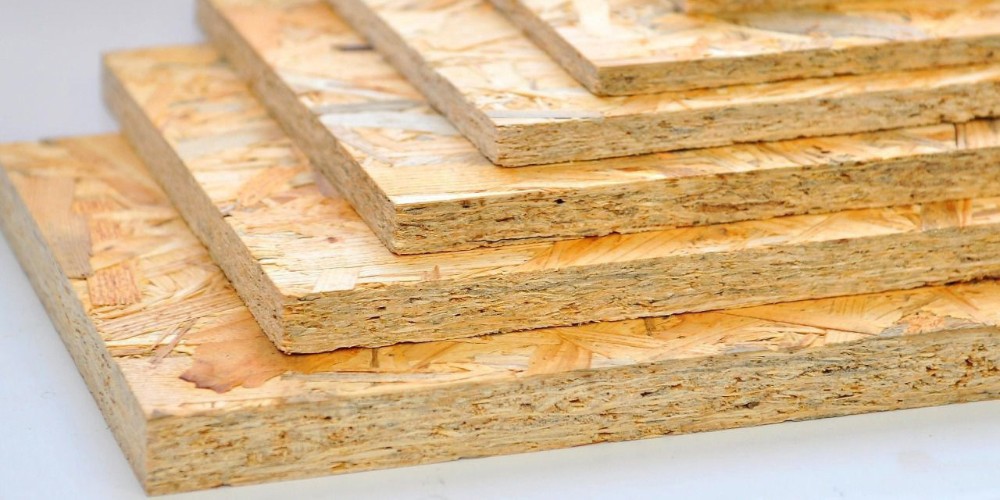
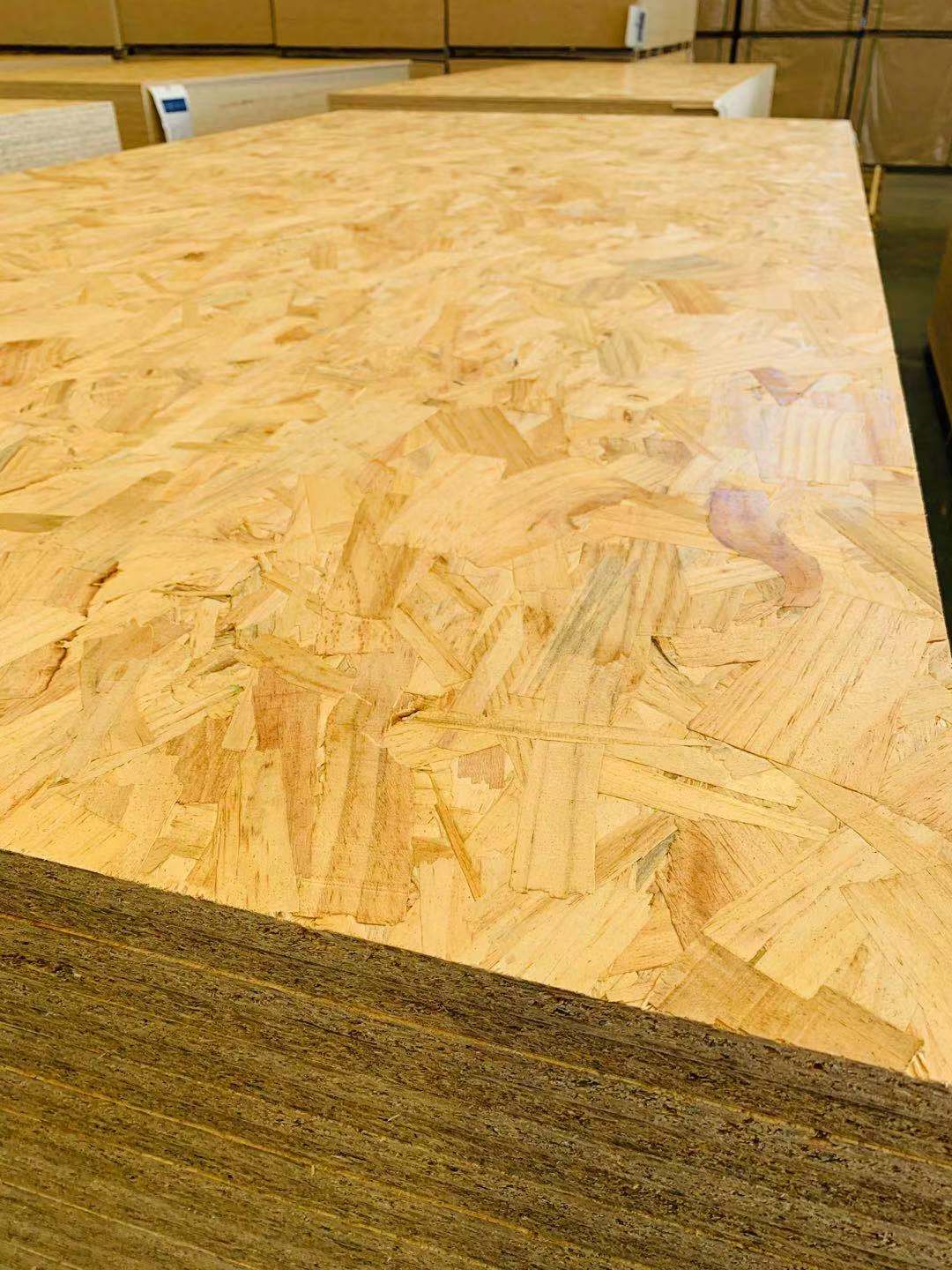





Advantages:
1) Tight construction and high strength
2) Minimum twisting, decontamination or warping
3) No rotten or decay, strong against corrosion and fire
4) Water proof, consistent when exposed in the natural or wet environment
5) Low formaldehyde emission
6) Good nailing strength, easy to be sawn, nailed, drilled, grooved, planed, filed or polished
7) Good heat and sound resistant, easy to be coated

Linyi YZY Interantional Trade Co,.Ltd,
Adress:Room 2204 Dongfang Jiayuan Building , Lanshan District,Linyi City Shandong Province,China 27600
Construciton Plywood Supplier |www.sowowood.com |
Skype:yzy@yzylinyi.com |Wechat:17753974353|What'sApp/Viber:+86 15094723345


















